| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Indicates no data available Indicates no data available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Indicates data exceeds plot scale. Indicates data exceeds plot scale. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
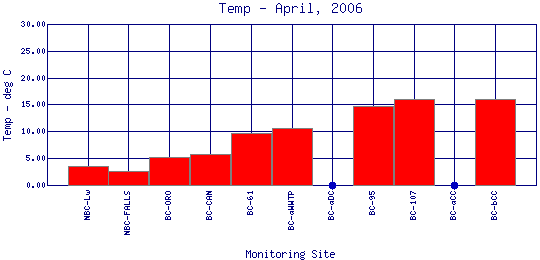
Temperature of water is a very important factor for aquatic life. It controls the rate of metabolic and reproductive activities. Most aquatic organisms are "cold-blooded," which means they can not control their own body temperatures. Their body temperatures become the temperature of the water around them. Cold-blooded organisms are adapted to a specific temperature range. If water temperatures vary too much, metabolic activities can malfunction. Temperature also affects the concentration of dissolved oxygen and can influence the activity of bacteria and toxic chemicals in a water body.
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
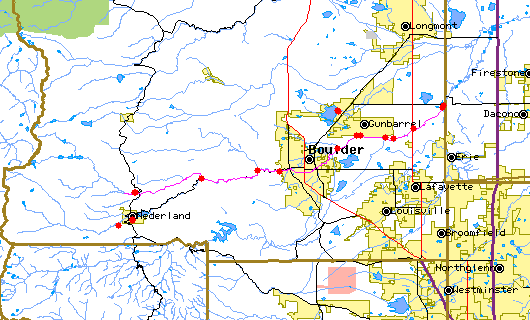
The above map indicates water quality monitoring sites. To view data at a specific site select it from the map with the mouse. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preliminary Data - subject to revision | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Return to the BASIN water quality catalogReturn to the BASIN environmental data catalog | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
About BASIN | Attribution | Feedback | Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
