| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Indicates no data available Indicates no data available | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Indicates data exceeds plot scale. Indicates data exceeds plot scale. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
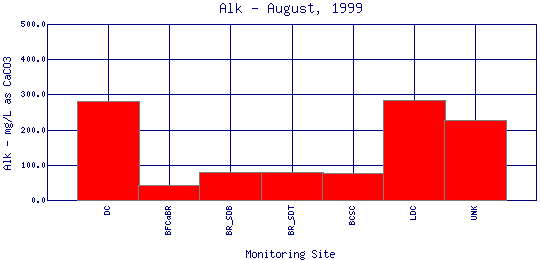
Alkalinity refers to how well a water body can neutralize acids. Alkalinity measures the amount of alkaline compounds in water, such as carbonates (CO3 2-), bicarbonates (HCO3 -), and hydroxides (OH-). These compounds are natural buffers that can remove excess hydrogen ions that have been added from sources such as acid rain or acid mine drainage. Alkalinity mitigates or relieves metals toxicity by using available HCO3 - and CO3 2- to take metals out of solution, thus making it unavailable to fish. Alkalinity is affected by the geology of the watershed; watersheds containing limestone will have a higher alkalinity than watersheds where granite is predominant. The Boulder Creek Watershed is composed primarily of granite rocks, thus the water has a lower alkalinity content. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||

| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
The above map indicates water quality monitoring sites. To view data at a specific site select it from the map with the mouse. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preliminary Data - subject to revision | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Return to the BASIN water quality catalogReturn to the BASIN environmental data catalog | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
About BASIN | Attribution | Feedback | Search | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
