 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Indicates no data available Indicates no data available | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Indicates data exceeds plot scale. Indicates data exceeds plot scale. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
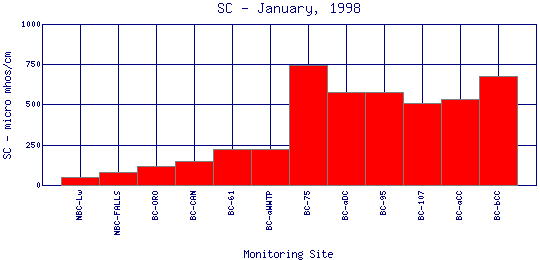
Specific Conductance is a measure of how well water can pass an electrical current. It is an indirect measure of the presence of inorganic dissolved solids, such as chloride, nitrate, sulfate, phosphate, sodium, magnesium, calcium, and iron. These substances conduct electricity because they are negatively or positively charged when dissolved in water. The concentration of dissolved solids, or the conductivity, is affected by the bedrock and soil in the watershed. It is also affected by human influences. For example, agricultural runoff can raise conductivity because of the presence of phosphate and nitrate. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
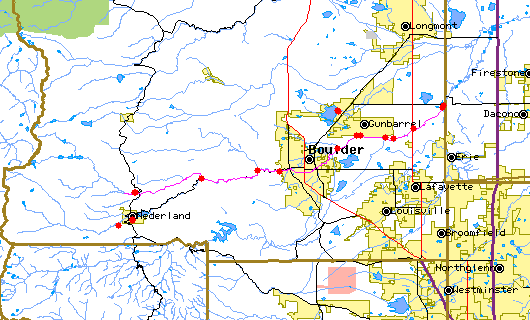
The above map indicates water quality monitoring sites. To view data at a specific site select it from the map with the mouse. | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Preliminary Data - subject to revision | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Return to the BASIN water quality catalogReturn to the BASIN environmental data catalog | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
| |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|
About BASIN | Attribution | Feedback | Search | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
